👋+: Mid-Autumn Meals: Winter Squash Edition
how to choose, store, and enjoy winter squashes + why I don't share meaty recipes
Allô! 👋
Welcome (back) to seasonal sundays, the supplement to good food at home where we take a closer peek at produce at its peak — with a short introduction, at least one recipe, and a (sometimes related) cooking Q&A. If you’d like to receive these letters straight in your inbox, feel free to hit the subscribe button below!
Happy Sunday! I hope these early days of November have been treating you well.
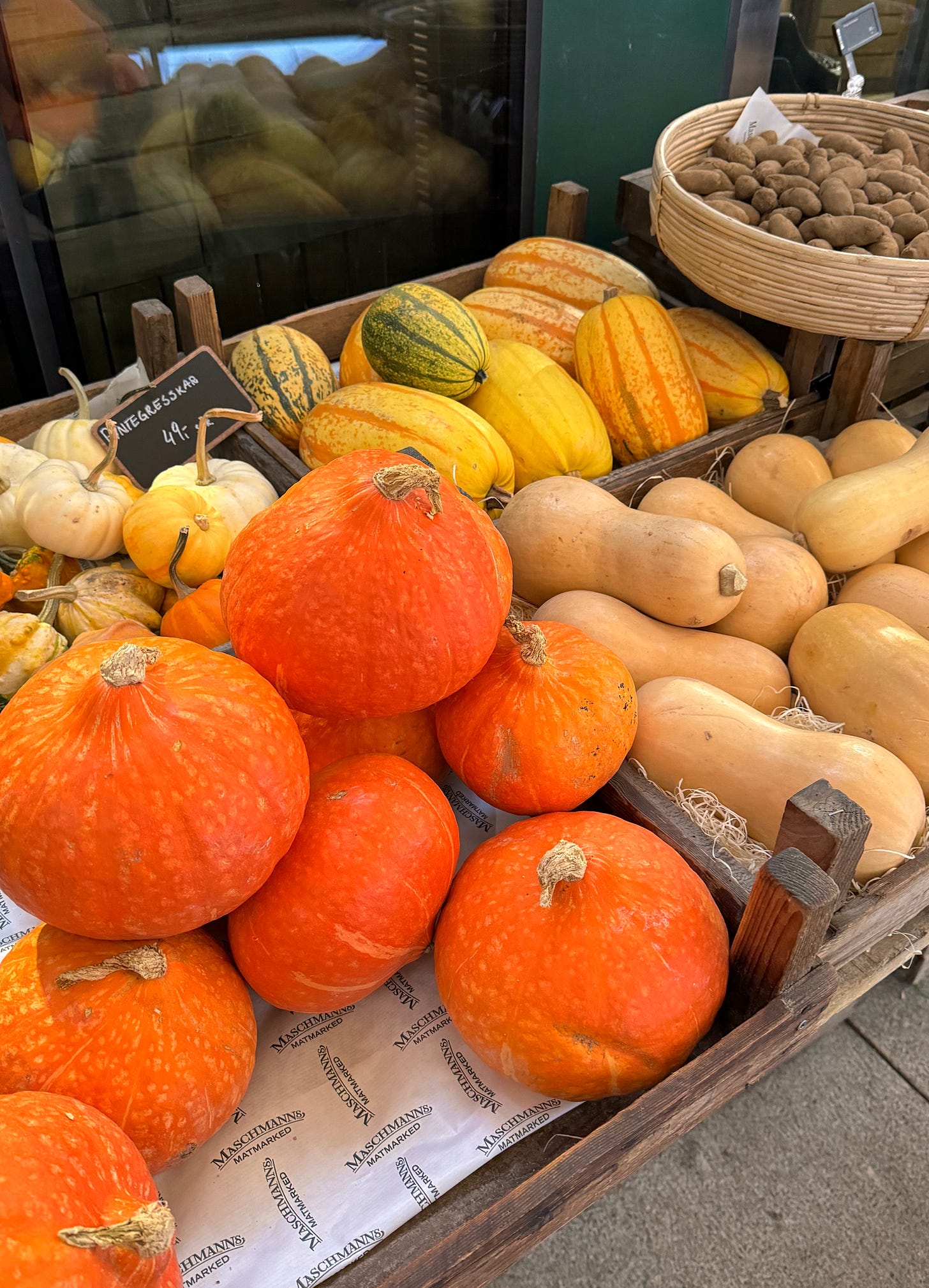
This week, we’re putting the spotlight on pumpkins, gourds, and autumn cucurbits of all kinds. I’m currently in the middle of a move (yes, another one) and half my things are in boxes, so I hope you’ll allow me a bit of “pumpkin retrospective”, so to speak — in addition to four new recipes, we’ll be exploring the best and easiest ways to use winter squashes via some of the season’s most popular and comforting dishes: soups, stews, pastas, pancakes, risottos, salads, and roasts.
On today’s newsletter menu, we’ve got an introduction to winter squashes, followed by two base recipes, plus ten recipes and ideas tailored to different winter squash varieties, and, to finish, a quick Q&A on why I don’t feature seafood or meat in my recipes.
Hope you’ll enjoy!
Wishing you a beautiful day and lots of gorgeous meals ahead
— Simone




P.S. If you enjoy this post, please do kindly give it a ❤️ — it really helps make it more visible so others can find it too!
While the season for harvesting pumpkins and other winter squashes is now mostly over, the time for enjoying them has only just begun. In late August and early September, when the first winter squashes were arriving on market stalls, we still had tomatoes, eggplants, plums, and melons to tantalise us. Now that November has arrived, however, winter squashes are at last leaning into their spotlight, proving themselves to be the true stalwarts we know we’ll be able to rely on, all winter long*.
*this is, in fact, how these cucurbits got their name — they are “winter squashes”, not because they grow or are harvested in winter (they don’t, and they’re not), but because they can be stored and savoured all winter long!
Some winter squash facts and tips you may find useful this season:
PEAK SEASONALITY
Early to mid-autumn.
AVAILABILITY
Late summer through to late winter, or even early spring.
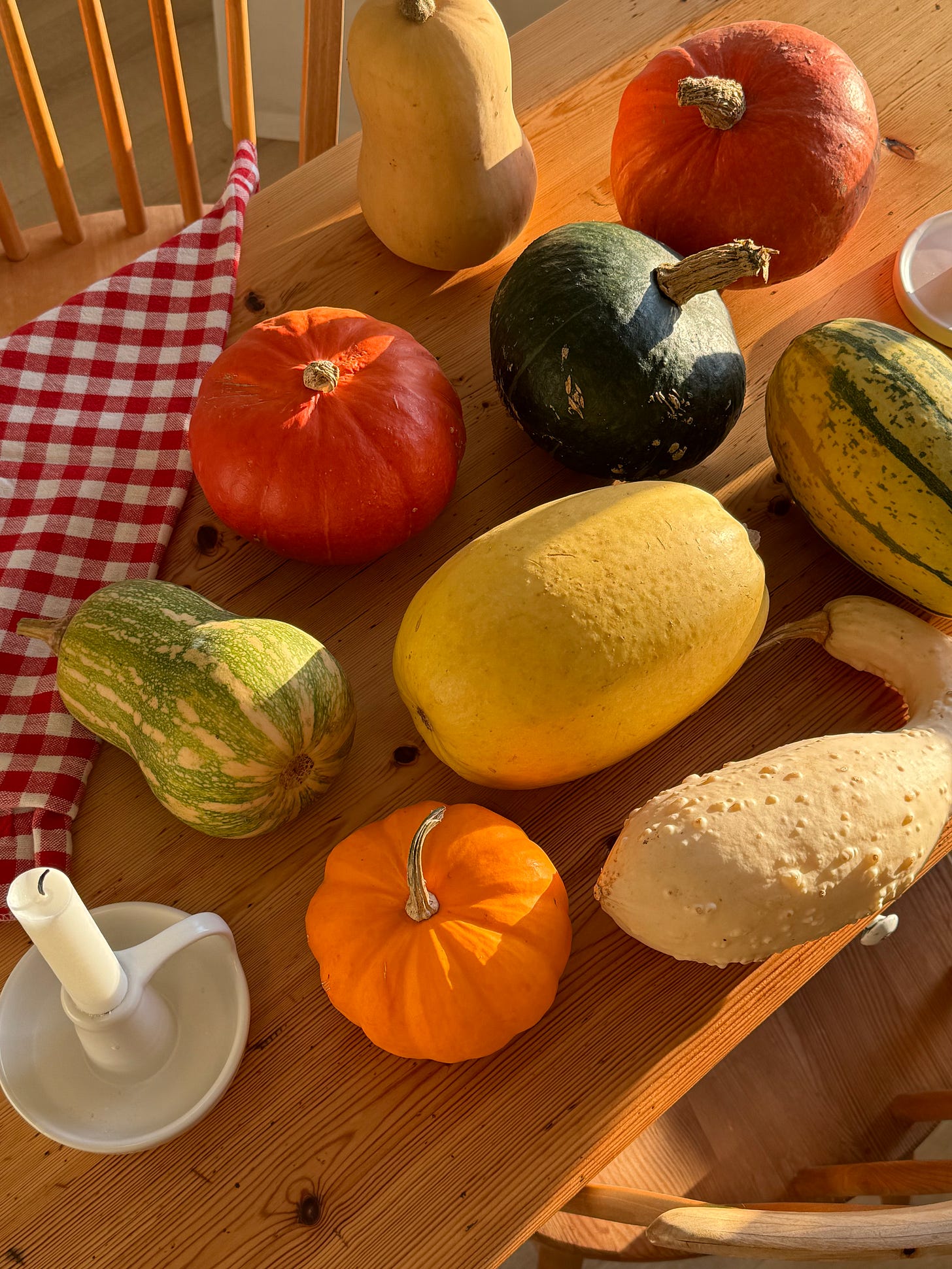
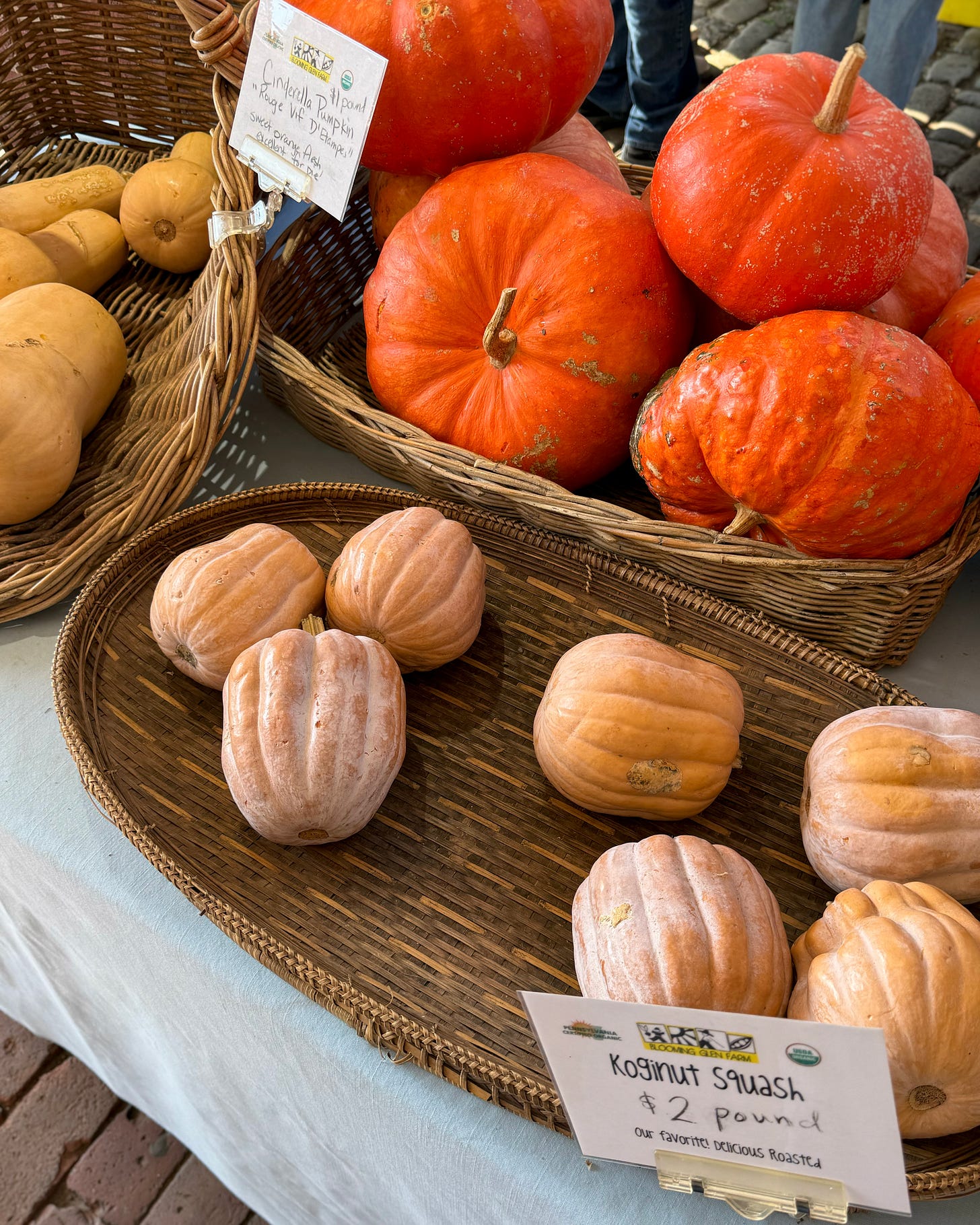
COMMON VARIETIES
Butternut squash
Red kuri squash / onion suqash / Hokkaido pumpkin
Delicata squash
Crown Prince pumpkin
Acorn squash
Delica pumpkin
Cinderella / Fairytale / Rouge vif d’Étampes
Kabocha squash
Sugar and pie pumpkins
Honeynut squash
Musquée de Provence
Hubbard squash
Spaghetti squash
Many more varieties exist, of course, but the ones above are among some of the most commonly sold for consumption, rather than decoration (though the edible kinds can also make for lovely displays).
WINTER SQUASHES: WHERE TO FIND THEM
Look for winter squashes at farmers’ markets or at farm stands (for the most uncommon varieties), at your local greengrocers and specialty grocery stores (for “gourmet” varieties), or in supermarkets (for the more familiar varieties).
WINTER SQUASHES: SHOPPING TIPS
Seek out winter squashes that are heavy for their size, with hard skins, and without any large soft, wrinkling, dark or discoloured spots. A ripe winter squash should make a hollow sound when tapped, and a well-cured one — i.e. one that has been properly dried for long-term storage — will have a long, hard dried-out stem (though note that not all winter squash varieties require curing). A few raised, dried-out, scars are usually fine (any undesirable bits can easily be peeled or cut away if you plan on eating the skin), and while pale spots from where the pumpkin lay in the field are not universal, they are completely normal and nothing to worry about. Squashes with missing stems or slight blemishes are still edible but do know that won’t keep as long, so plan to use these sooner.
WINTER SQUASHES: STORAGE & SHELF-LIFE
Most whole winter squashes should be kept in a cool, dry place† (10–15°C / 50–59°F at 60–70% humidity, if you can measure it) — ideally in a cardboard or vegetable crate, up on a shelf or off the ground if you can, making sure to leave a bit of a gap between each squash. Once cut, wrap a winter squash well, store it in the refrigerator, and cook it within 3–5 days.
If you want to be sure that your winter squashes are well-cured before storing them, you can place them on a rack somewhere well-ventilated, dry, and warm (even sunny) for up to 7–10 days before transferring them to cool storage. Check on stored winter squashes weekly, making sure to remove and eat any with developing blemishes or soft spots first.
Note that different varieties will have different shelf-lives. While varieties like acorn and honeynut squash will generally only keep for up to 4–5 weeks, spaghetti, butternut, and kabocha squash varieties usually have shelf-lives ranging from 1–3 months, and others like Hubbard tend to store for up to 6 months. Other varieties, like Jarrahdale, can even last up to 2 years!
†One exception is acorn squash, which generally is not cured as the process reduces its shelf-life and quality, and therefore requires cooler temperatures for storage.
WINTER SQUASHES: AROMA & TASTE
Sweet, starchy, and nutty; not unlike a cross between a sweet potato and a dry, floury potato (depending on the variety and squash type). Some are buttery, others earthy or musky; some very sweet and flavoursome, others mild and a little dry. A few varieties are stringy and rather flavourless, while others are outright bitter — these decorative types are often described as “ornamental only”, even though all winter squash varieties are entirely edible (you just may not want to bother cooking with some of them).
WINTER SQUASHES: USES & PREPARATION
Although every part of a winter squash is edible, some varieties have thick skins that can be unpleasant to eat. Most thin skins can be eaten, or removed before cooking simply by peeling away with a vegetable peeler — while thicker, knobbly skins are usually easiest to remove after cooking (though you can also cut them away before cooking if that’s more suitable). Dried stems are always best removed before cooking, and can usually be knocked off with the back of a knife.
Pumpkins and other winter squashes are most commonly cooked — steamed, roasted, fried, or even grilled — to be eaten right away, but are also marvellous simmered in brine and left to pickle in a jar, processed into sweetly spiced jam, or even dehydrated into pumpkin “chips”, “leather”, or powder. Many varieties also taste quite nice raw, though you’ll want to thinly shred or shave them (as with beetroot or kohlrabi, say) to make them more digestible.
Personally, I’m more of a cook-and-enjoy-straight-away type of winter squash aficionado.
Below are two base recipes I turn to over and over again when I want to cook with winter squashes, plus ten dishes to use them in, each featuring different varieties best suited to them:
base recipe one
WINTER SQUASH PURÉE
yields approx. 55g of purée per 100g of winter squash / 1 US cup of purée per lb of squash
You’ll need:
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to good food at home to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.